View Structure¶
In a user panel, every view draws the main window no matter whether it is selected from a static navigation tree or dynamically navigated to. This is a set of documents to specify the APS JS SDK components of a view, layout rules, widget hierarchy, widget base properties, and the ways to load widgets.
In this document:
Typical Operations¶
In a screen, users need to perform various operations with objects, including:
Creating objects
Updating objects
Listing objects and deleting objects in lists
Monitoring and processing events that can happen with objects
View Components¶
With the help of APS JS SDK, the typical view is built from several groups of control elements (controls).
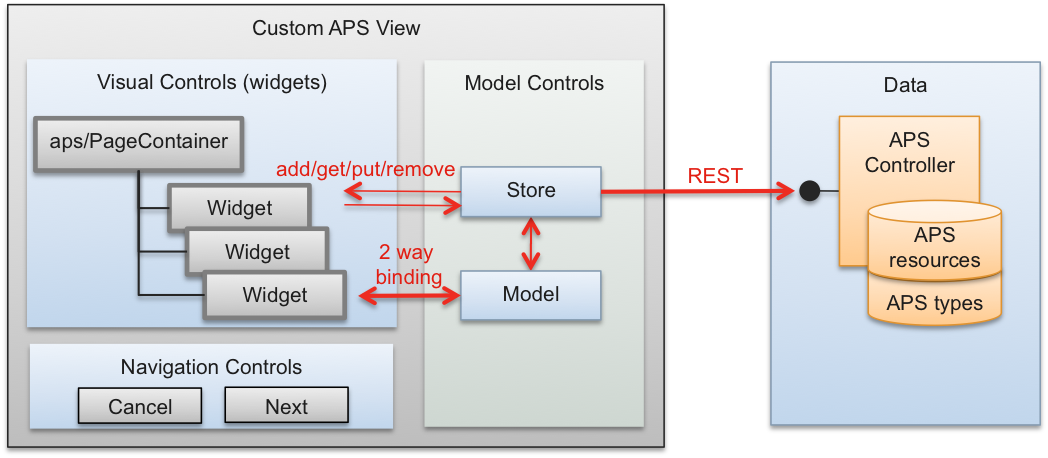
Visual controls are defined and processed by HTML and JS code:
The
aps/PageContainercontrol is the root element in a view that contains all visual controls. Only onePageContainermust be defined in the view.Widgets are inserted into the
PageContainer. They allow a user to perform all necessary operations with application resources.
Navigation controls, presented by the
Cancel,Previous,Next, andSubmitbuttons, can be declared in the application metadata, but processed by the JS code. The JS code decides where to navigate to and which other actions to perform when a control is activated.Model controls are used for effective management of data in the user browser and for interacting with the APS controller:
A
Storemanages the asynchronous communication with the APS controller. It implements the REST operations: POST, GET, UPDATE, and DELETE.A
Model, if bound to a widget, establishes the 2-way synchronization with the widget. If the widget value is changed, it will be synced with theModel. Usually, when navigating to another view, the JS code takes care of syncing the Model with the Store control and saving the data in the APS database.
SDK Interfaces¶
In accordance with the list of control groups considered above, APS JS SDK provides three API groups.
View API is used for creating and managing visual controls (widgets), for example:
aps/Gridallows you to present tables and toolbars. It can also split tabulated data into pages, allowing for navigation through them, filtering, sorting, and row selection.Input controls, such as
TextBox,Select,Slider, andCheckBox, allow users to enter or select required data.Output controls, such as
aps/ActiveList,aps/Gouge,aps/Message, andaps/ProgressBar, are needed to display output data for users in a convenient way.
Model API exposes two objects for managing data:
Modelis a data model for representing APS resources. It is used for syncing resource properties with widgets.Storeis a data store used for communicating with the APS controller.
Navigation API implements dynamic navigation between views by means of the following functions:
gotoView()switches a screen to the specified view.onSubmit(),onEdit(),onCancel(), and other event handlers are used by the JS code to process activation of different navigation controls.
Widgets¶
APS JS SDK provides a set of modules for creating and using various visual interface elements of web applications, such as interactive buttons, sliders, toolbars, and progress bars.
Note
For the full description of all APS JS modules refer to the JS Modules reference guide.
Before you start creating your application UI using APS JS widgets, be aware of the following general documents:
Layout Rules: the nesting rules for widgets
Layout Code Examples: demo code for typical layouts
Declarations: various ways to define and load widgets
Also, for your convenience, we recommend you get familiar with these common widget properties and methods:
Base Properties and Methods - properties and methods common to most widgets
Widget Categories - widget categories as well as category specific properties and methods
Control Panel Specifics¶
Depending on the user panel type, the view structure varies significantly as specified in the following documents:
