Mail Notifications¶
The platform built-in Messenger Manager service based on the APS type MessengerManager enables applications to register their own email notification templates and then send email notifications based on those templates to subscribers of that notification.
In this document:
Email Templates and Message Types¶
The platform contains a set of predefined email templates used to notify users about some events inside the platform or in the integrated services. A user can be subscribed to notifications based on those templates.
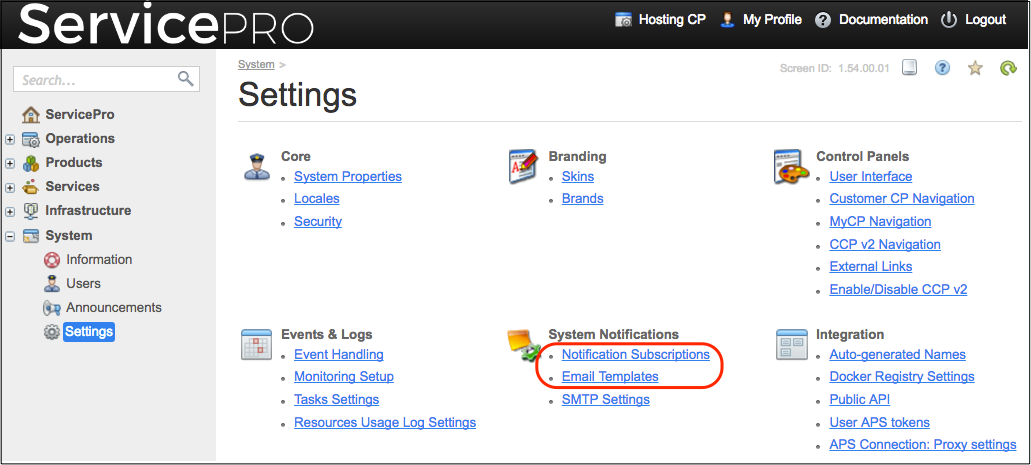
In the platform control panels, an email template represents a registered message type and a set of sections containing the localized message subject and body for the locales activated in the platform. An email template must define the notification subject and body for at least the English locale. The providers can modify some of the fields; they can also translate the subject and message body in the locale sections.
Note
The English locale is mandatory in an email template. If no other locales are defined in a message type the subject and body of the English locale are copied to all other locales.
A message type contains several fields and provides some variables, for example, ${domain_name},
assigned when a notification based on that message type is sent:
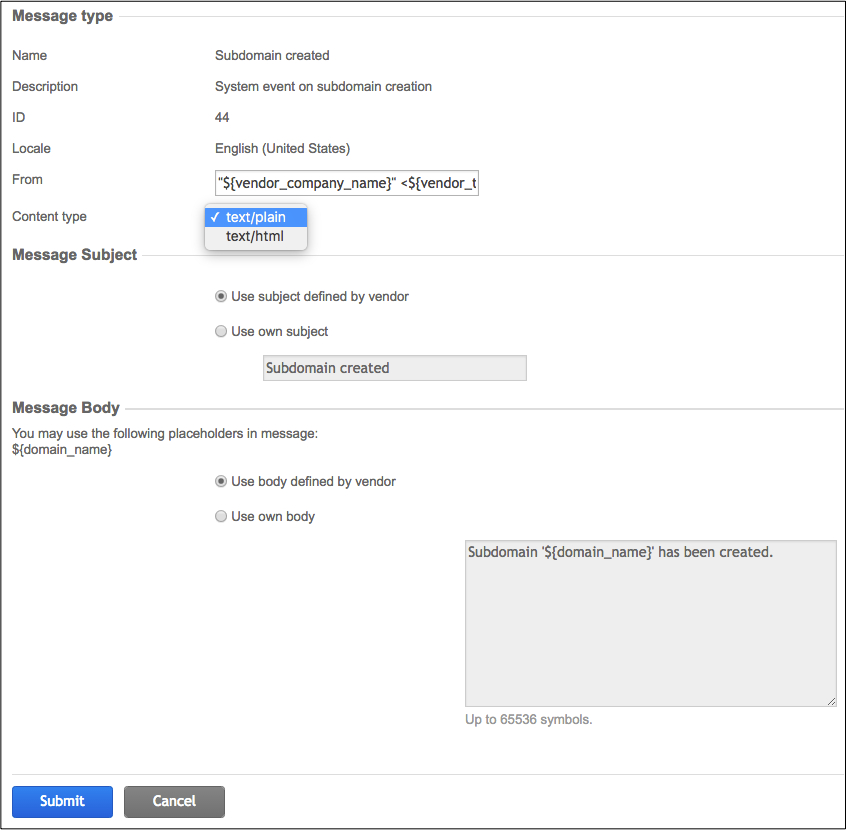
The Content type informs the system whether the message body is interpreted as
a plain text or parsed as an HTML code.
When using the text/html content type, there is no need to enclose the message into the HTML <body> tags.
However the message body typically contains other markup tags, for example, <h1>, <p>, and <b>.
An application can create its own message types containing the above-mentioned fields and declare its own variables in those types.
Typical Procedure¶
Typically, an application registers its message types during the installation of an APS application instance and then sends notifications from its scripts implementing the provisioning logic. Therefore, a typical procedure for an application consists of the following steps:
Message types registration. A message type may contain variables whose values the application defines when it sends a message. To register a message type, an application calls the
addMessageTypemethod of the MessengerManager service and sends it a message type with the following content:nameis an arbitrary (but globally unique) name assigned to the message type.Note
The platform differentiates message types and the respective email templates by names. This means that if an application registers two or more message types, the latest registration overrides all previous message types that use the same name.
descriptionis a brief general description of the message type to show it in a platform control panel.subscribeByDefaultspecifies if by default a new user will be subscribed (true) to notifications of this type or not (false).contentTypeis an enum variable that can be either “text/html” or “text/plain”.templatesis an array ofTemplatestructures. Each structure represents a locale and contains the following strings:localespecifies a locale, for example, “en_US”.fromis the email From header.subjectis the subject of the email notification translated to the corresponding language.bodyis the translated notification body. This is the actual description of the occasion.
When registering a message type, the application should store the ID under which the type was registered in the platform. The application will need that ID to send notifications based on the message type.
Sending of the notification. An application sends the notification by calling the
sendMessagemethod of the MessengerManager service. When calling this method, the application must pass an argument as aMessagestructure with the following content:msgTypeIdis the ID of the registered message type.accountIdoruserIdis respectively the APS ID of an account or a user and this way it specifies the addressee to whom the platform will send the notification as explained in the MessengerManager document.paramsis a named list of variables with assigned values.
Registration¶
APS PHP Runtime Tools¶
To help applications register a message type, the APS PHP runtime provides the following components:
Class
MessengerManagerwith the full path\com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\MessengerManager()provides access to the MessengerManager methods.Class
Templatewith the full path\com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\Template()defines theTemplatestructure as declared in the MessengerManager APS type.Class
MessageTypewith the full path\com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\MessageType()defines all components of a message type to be registered. It includes an array of theTemplatestructures to present various languages.
Example¶
For example, an application must notify the customer staff about a new subscription that provides the application services.
When provisioning an APS application instance, the application root service called clouds registers a message type
in English with the text/plain content type.
In our example, the application’s scripts/clouds.php file contains the following additional definitions
for the clouds service:
To save the ID of the registered message types, the class declares an additional property:
/** * @type(string) */ public $newSubscriptionNotificationId; # To store the ID of the registered message type
The following private function creates and registers a message type in plain text format for the English locale, as specified in the
templatestructure:private function registerMessageType() { # Get connection to the Messenger $resources = $this->getAPSC()->getResources('implementing(http://www.parallels.com/pa/pa-core-services/messenger-manager/1.0)'); $messengerManagement = new \com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\MessengerManager(); $messengerManagement->aps = $resources[0]->aps; # Prepare the message type for the English locale in the plain text format $template = new \com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\Template(); $template->locale = "en"; $template->from = '"${vendor_company_name}" <${vendor_tech_email}>'; $template->subject = "New VPS Demo subscription"; $template->body = 'The customer ${customerName} subscribed to the VPS Demo application. Subscription APS ID - ${subscriptionId}'; # Prepare the full message type to send a Plain Text content $textMessage = new \com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\MessageType(); $textMessage->name = "New VPS demo subscription"; $textMessage->description = "New VPS demo subscription is created"; $textMessage->subscribeByDefault = true; $textMessage->contentType = "text/plain"; $textMessage->templates = array($template); # Register the message type $textMessage = $messengerManagement->addMessageType($textMessage); $this->newSubscriptionNotificationId = $textMessage->id; }
Note
The registered message type declares two variables:
customerNameandsubscriptionId. When sending a notification, the application must specify the values of those variables.Finally, the standard
provisionmethod calls the private function to register the message type:public function provision() { $this->registerMessageType(); }
In accordance with this example, the application will register its message type during the application deployment on the platform. Once an APS application instance is installed, the provider will see the new email template:
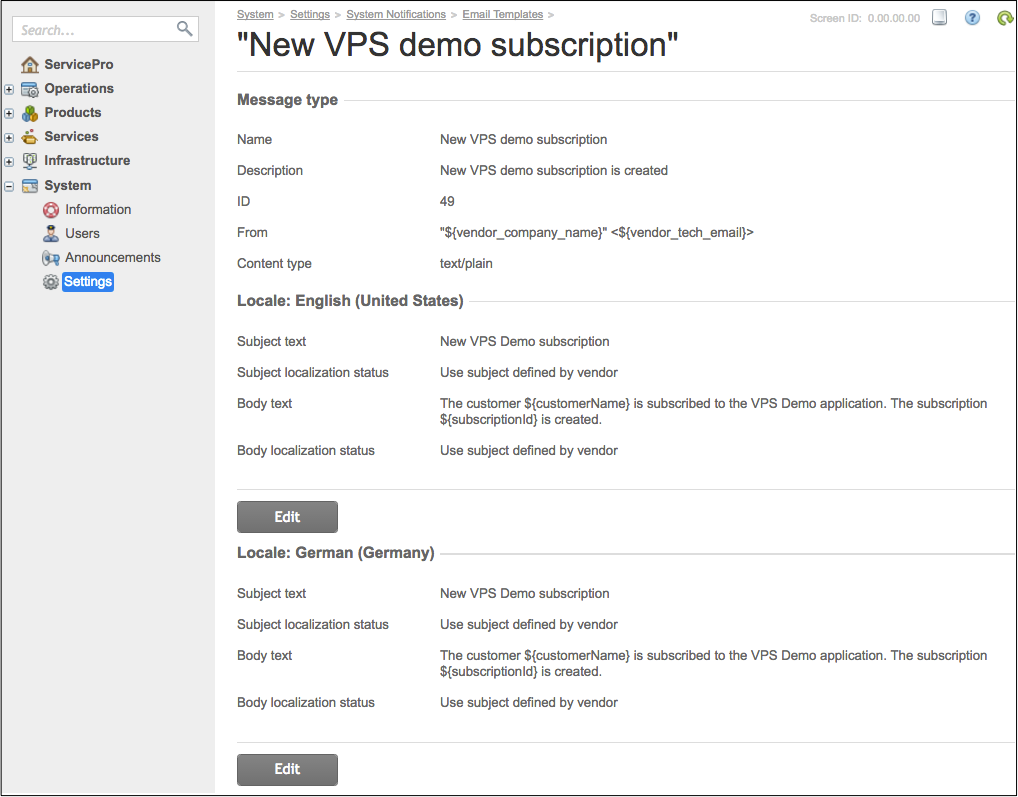
In the same way, an application can register message types for other occasions, such as provisioning of resources or changing a resource state.
Sending Notifications¶
Using its registered message type, an application can send notifications to the staff and service users of the customers subscribed to the application services.
APS PHP Runtime Tools¶
To help applications send an email notification, the APS PHP runtime provides the following components:
Class
MessengerManageris the same as is used for the registration.Class
Messagewith the full path\com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\Message()defines theMessagestructure as declared in the MessengerManager APS type. It must specify the following:msgTypeIdis the ID of the message type registered earlier.accountIdmust be specified to send the notification to all staff members of the specified account.paramsis a named list that assigns values to the variables declared in the registered message types.
sendMessageis the method defined in theMessengerManagerclass that sends the preparedMessagestructure through the APS controller.
Example¶
Continuing with the scenario started in the previous example, the application
defines the service for its management context APS type (it is auto-provisioned, that is, started
along with the creation of a new subscription) as follows:
class context extends \APS\ResourceBase {
## Strong relation (link) to the application instance
/**
* @link("http://aps-standard.org/samples/mail/cloud/1.0")
* @required
*/
public $cloud;
## ... Other properties and methods
## Private function to send notifications
private function sendNotification() {
$resources = $this->getAPSC()->getResources('implementing(http://www.parallels.com/pa/pa-core-services/messenger-manager/1.0)');
$messengerManager = new \com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\MessengerManager();
$messengerManager->aps = $resources[0]->aps;
$message = new \com\parallels\www\pa\pa\core\services\messenger\manager\Message();
$message->msgTypeId = $this->cloud->newSubscriptionNotificationId;
$message->accountId = $this->account->aps->id;
$message->params = array(
'customerName' => $this->account->companyName,
'subscriptionId' => $this->subscription->aps->id
);
$messengerManager->sendMessage($message);
}
## Send a notification when a subscription is created
public function provision() {
$this->sendNotification();
}
}
Key:
- The management
contextresource has a relationship with its application instancecloud. The latter enables the script to get the ID of the registered message type using the link$this->cloud->newSubscriptionNotificationId. The private function establishes a connection to the APS controller, then assigns values to the required properties including a set of variables (
params). Finally, the function sends the prepared message by calling thesendMessagemethod.
Similarly, an application can register message types and send notifications on various other occasions using the proper provisioning scripts.
