Table Of Contents
Application Packaging Standard
Last updated 18-Mar-2019Unprovisioning Resources¶
When there is a need to remove a resource, a REST DELETE request should be sent to the /aps/2/resources/{ID}
URI of the APS controller, where {ID} is the resource ID.
The controller, in turn, will request the unprovision method on the application service by forwarding
the DELETE request to the URI similar to https://endpoint/service1/{ID}, where service1 is
the application service responsible for the resource type and ID represents
the identifier of the APS resource that needs to be deleted.
An application can remove a requested resource synchronously (within a few seconds) or may request the APS controller to switch to the asynchronous mode similar to the algorithm described in the Provisioning Resources document.
In this document:
Synchronous Unprovisioning¶
The DELETE operation sent from a user requires the APS controller to resend it to the APS application endpoint as presented in the following diagram.
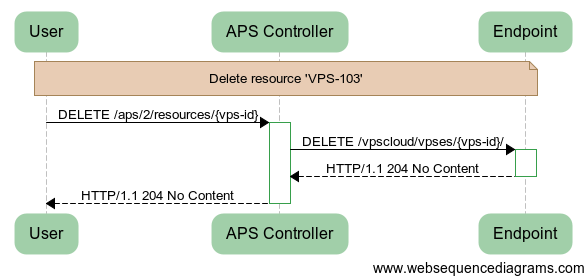
Examples of the REST messages are presented below.
Request to APS controller:
DELETE /aps/2/resources/7ab1be46-a02c-414c-a44a-88b199ba9047
Request from APS controller to application service in assumption that /vpscloud/ represents the application
endpoint base URI and vpses is the resource factory (application service):
DELETE /vpscloud/vpses/7ab1be46-a02c-414c-a44a-88b199ba9047
Response from the application service to APS controller:
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Response from APS controller:
HTTP/1.1 204 No Content
Asynchronous Unprovisioning¶
If the application cannot remove the requested resource immediately, it can return the 202 Accepted code to request more time for the completion.
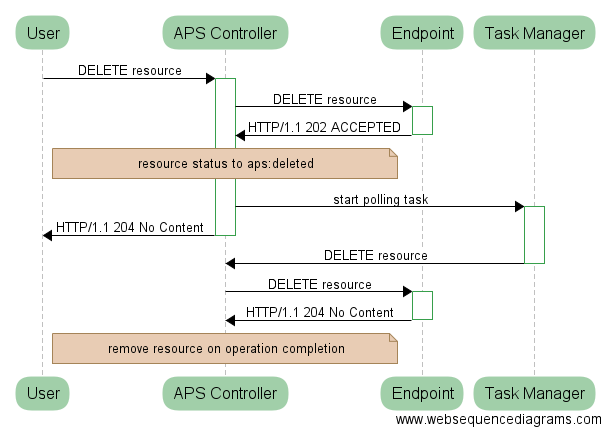
The APS controller changes the resource status to aps:deleted and requests the task manager
to schedule a task triggering the next request for the DELETE operation.
This continues until the application returns the 204 No Content status to the APS controller.