Table Of Contents
Application Packaging Standard
Last updated 18-Mar-2019SDK Overview¶
If you start using the platform SDK, this is the first document that you should study.
In this document:
Get Started Scenarios¶
If you are familiar with the APS integration principles generally and want to start practicing in the APS environment, follow these scenarios:
- Get Started - directs you through the step-by-step process of creating your first APS application. The scenario includes the simplified design, development, deployment, provisioning, and update of the application.
- Using APS REST API - helps you get started using the APS REST API to manage directly the platform services and resources of the integrated APS applications.
Introduction to APS Services¶
Distribution of cloud services to businesses is simpler through Hosting Providers, Telecommunication Companies and Value Added Resellers – Service Providers. With this channel, an Application becomes available to millions of existing customers across the globe. You can focus on improvements of your technology, while Service Providers take care of your business growth.
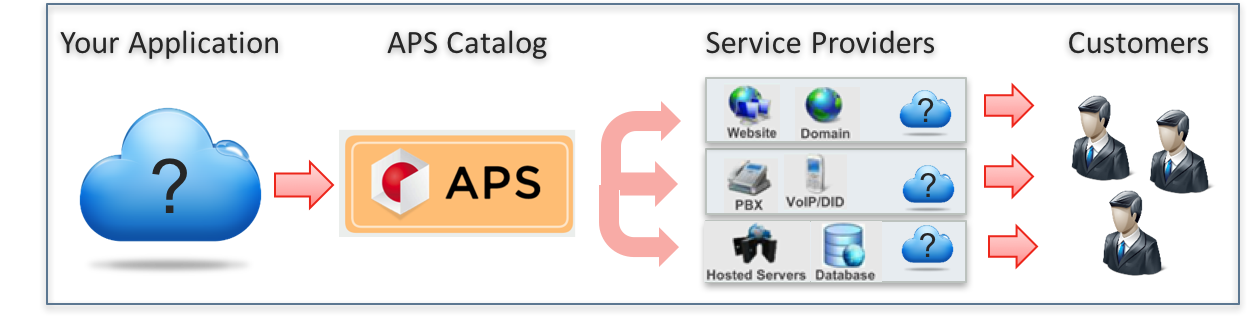
Odin Automation is a service automation platform that provides its internal Application Packaging Standard (APS) controller as a way for independent software vendors (ISV) to distribute cloud services through service providers.
Note
In Odin Automation, APS is a unified method to integrate applications and third-party management systems regardless of their complexity.
APS allows various cloud service vendors to integrate their applications with the platform through an integration APS package created for each application. The applications can collaborate with different cloud services through the standardized RESTful API within the APS ecosystem.
APS packages, certified as APS-compliant, are usually stored in the APS catalog, which makes them available to any service providers.
- Application developers working for independent software vendors (ISV)
- They wish to sell their cloud services.
- For this, ISVs need to develop the respective APS applications (APS packages) as integration part of applications in a standard way.
- Operations and support teams working for service providers
- They need to implement and support APS applications on their hosting automation platforms.
- Third-party developers working for system integrators (SI) who wish to build their business on APS
- They are going to integrate existing applications with the hosting platform and provide APS packages as ready-to-use cloud solutions.
- SIs sometimes need to integrate 3rd party management or provisioning systems with Odin Automation.
APS Ecosystem¶
In Odin Automation, integration with applications is implemented by means of the APS ecosystem.
The platform contains a special module called APS controller that provides to applications a RESTful based bus for exposing application endpoints to be used by other applications and management systems.
Note
The APS controller functions as a message broker - all APS REST messages go through it.

All participants on the APS bus are split into two groups:
- APS services - they expose their endpoints to provide application resources to the platform accounts. The group includes not only cloud applications integrated through APS connectors but also some modules (services) of the platform.
- Service management systems (3rd parties) - they interact with APS services to monitor and manage the resources of the platform and the integrated applications.
The interaction between the integrated components goes through the APS controller. The latter stores the presentation of application resources as APS resources (objects) in its database.
The platform services are available for other integrated systems and applications as integration points, for example:
- Account management
- User management
- DNS management
The platform user interface (UI) is provided through the provider control panel (PCP) and customer control panel (CCP v1 and CCP v2). Any integrated application can extend the control panels by adding their navigation panel with custom UI views.
Integrating Applications¶
An application is integrated into the APS ecosystem through a special integration component, known as APS application. The latter consists of:
- APS connector - a backend gate between the APS controller and the application services that implements the application provisioning logic.
- Custom UI - a set of frontend UI views for users to manage the application resources.
- Metadata and schemas - declaration and definition of the application resources, services, and UI components.
To integrate an Application with the platform, the Application integrator should develop an APS package that allows providers to deploy the respective APS application on their platforms.
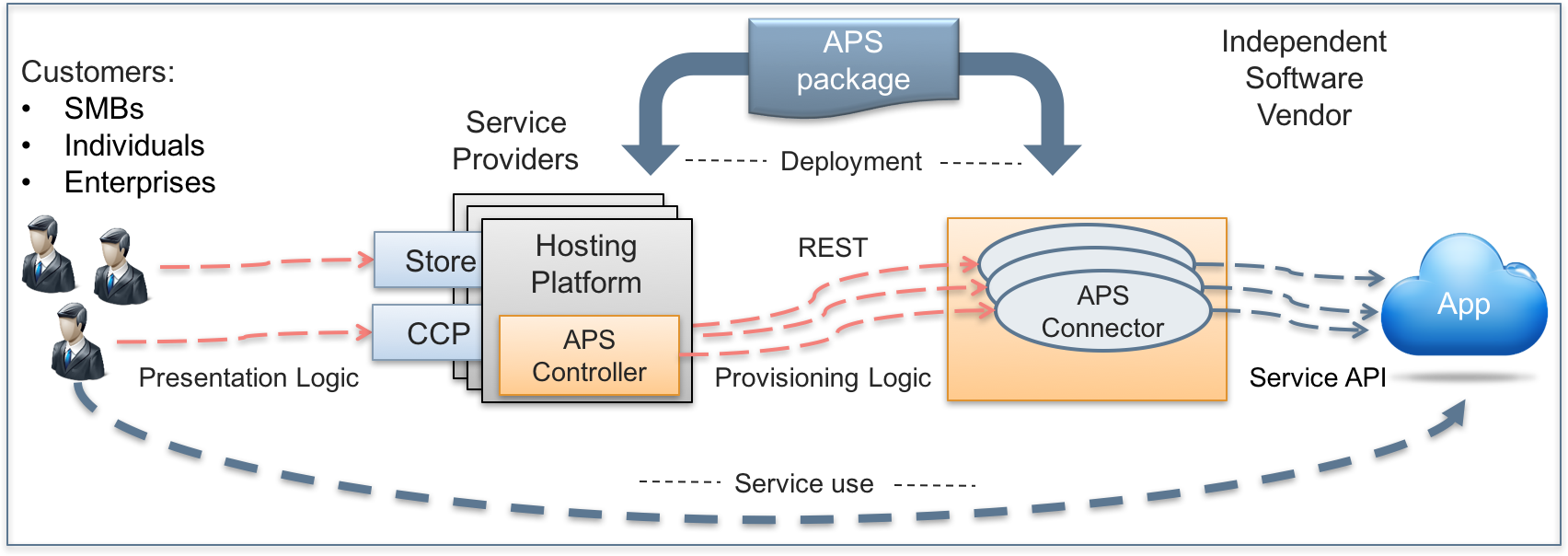
The APS application life-cycle includes the following steps:
- An integrator develops an APS package that ships all components of the APS application
including:
- Meta declaration of APS resource types, services, and custom UI components.
- Provisioning logic that allows the APS controller to interact with the application on backend. This logic exposes the application services used to manage the application resources, that is create, update, and remove the resources. You can develop the provisioning logic using any programming language. For PHP code, we recommend using the APS PHP framework that substantially simplifies the integration with APS.
- Presentation logic (also known as User Interface or UI) containing JavaScript views based on the APS JavaScript SDK that will allow the providers, customers, and users to manage the application resources in a comfortable way.
- A service provider uses the APS package to deploy the APS application on the platform.
Usually, all APS application
components are shipped inside the APS package. The whole package must be imported to the platform
and its provisioning logic is deployed as a separate APS connector. If the provisioning logic
is written in PHP, then the APS connector is typically deployed on a host with
installed APS PHP framework (runtime).
On completion of this stage:
- The platform will be aware of the resources the Application can provide. The operations team will be able to manage Application services (resources) through the custom UI of the integrated Application.
- The platform will be able to interact with the Application by using REST API. The APS connector installed from the APS package or from another source will process REST API calls on the one side and interact with the Application through its original API on the other side.
- The platform will be able to sell Application services through its store.
- The service provider sells and upsells Application resources separately or in combination with other resources.
- Customers consume the Application services. The customers subscribed to the Application resources through the online store* will use the customer control panel (CCP) with the plugged application custom UI to provision and manage the application resources (services). Particularly, a customer can assign an application service to service users who will be able to consume the service directly through the corresponding service API.
In the Application life-cycle inside the APS ecosystem, an integrator needs to complete the first step, that is, to develop an APS package for the Application they want to integrate with the platform. Using this package, service providers will be able to deploy the Application and sell the Application services to many customers.
Getting Familiar with Platform¶
Cloud Service Automation¶
Odin Automation is the leading hosting and cloud services delivery platform used by thousands of service providers worldwide, from the largest telecom operators in the world to top hosters and providers of vertical solutions.
The platform combines Operations Support System (OSS) and Business Support System (BSS). In the simplest case, you may use a test platform containing only OSS installed on a single host called management node.
The platform uses the APS technology for application service delivery. Assuming that you have some developed APS packages, you will need to go through the rest of the application life-cycle stages to complete the integration with the platform:
- Application deployment - make the application ready for providing services on the platform.
- Application provisioning - create customer subscriptions and provision application resources for customers.
The platform provides all necessary services for it as described in the following sections.
Platform for Testing and Education¶
For testing APS applications and for training, we recommend that you use a separate test platform. In the simplest case, it consists of the OSS part on the management node without the BSS. You will need the BSS, when testing the integration with the platform commercial integration points.
If you do not have such a test platform yet, register your company and yourself in the APS development portal and then order a sandbox with the simplest configuration without BSS, that is “lin-mn” configuration, or with the complete configuration, for example, “lin-pba”, by following the corresponding procedures.
Account Management¶
You can get started by using two major account types - provider and customer.
There is only one account of the provider type who is the owner of the installed platform. On the newly installed platform, you have a user whose login name is
adminand the password specified by you during the installation. Log in to the platform using theadmincredentials. For example, if the domain name you assigned to the management node isa.isv1.apsdemo.org, enterhttp://a.isv1.apsdemo.org:8080in the address field of your browser and then log in asadmin.Note
HTTP on port 8080 is available only from the private network where the management node is installed. If you ordered an APS sandbox, you can access that network through a VPN channel. The access from the Internet to a production system is available through HTTPS only.
You will get access to the OSS provider control panel (PCP).
If BSS is also installed, you can switch to the BSS provider control panel and then switch back to OSS.
The provider can create any number of customers. Every customer normally has an administrator (staff member), who has necessary permissions to manage all customer resources. The administrator can log in to the customer control panel (CCP) using the same URL as the provider but entering their own email address as the login name. If necessary, the administrator can create any number of service users (end users) and assign services (resources) to them. Any of those users can get access to their own control panel, called MyCP, using their email address as the login name.
Resource Model¶
This section concerns application services and resources provided by them. We do not consider the application user interface (UI) here.
APS Application API¶
An APS package contains a declaration of the APS application API by means of APS types. For each APS application service, the package declares an APS type (one-to-one relation) with the following typical definitions in JSON format:
- Resource schema containing properties and structures used by the service to create and manage resources based on this type. Also, the type defines relationships with resources of other APS types.
- APS operations that the service can perform, including generic CRUD (create/provision, read/get, update/configure, and delete) and custom operations on resources.
Installation of APS Applications¶
You can consider a cloud application as integrated into the APS ecosystem only after the provider establishes a secure connection between the platform and the original service API. Also, the platform must incorporate a custom application UI to manage the application services.

Installation of an APS application requires the following steps:
- Import the APS package to the platform - the APS types are copied to the APS database.
- Create an APS connector - installation of the backend (provisioning) logic on a host called endpoint host on the diagram.
- Install the APS application instance on the APS connector - a trusted connection is established between the APS
controller and the application through the APS connector. The APS controller creates the respective
APS resource using the APS type
Appas the resource schema.
An APS connector must have a connection with the cloud application. It will convert the REST requests from the APS controller to the original API calls of the cloud application.
Generally, an APS package declares the following APS types:
- The type with the application root service definition - this is a mandatory type contained in any APS application and used to create an APS application instance on an APS connector.
- APS types used to provide a shared set of parameters for resources of other APS types - parameterized services.
- APS types used by subscribers to create their own individual resources. Some parameters of a new resource are copied from a shared APS resource selected by the subscriber.
Pay attention to the built-in APS specific resource classes described in the next section.
Resource Types¶
To provide any service, the platform must have a resource type describing the service specifics by means of activation parameters. For APS applications, there are two resource classes used to create two groups of resource types:

- Application Service Reference resource class creates resource types for providing shared APS resources called
service profiles and also known as parameterized services or offers.
The service profiles belong to the provider and allow subscribers to choose a proper service level when creating
resources from the Application Service class. For example, the provider can create a number of offers
(“silver”, “gold”, and “platinum” configurations)
with different service levels (parameterized service). Typically, the provider must go through two steps:
- Create the needed number of the service profiles (offers).
- For each service profile, create a resource type from the Application Service Reference resource class.
- Application Service resource class creates resource types bound to APS types. Subscribers will use those resource types to create their own individual resources. As mentioned earlier, such a resource can be bound to a service profile to set some parameters from that profile.
Service Template¶
The provider can subscribe customers to services only through a service template that must contain all resource types the provider is going to sell.

For each resource type in a service template, the provider must set a limit. If a resource is unlimited,
its limit property in the service template is set to -1.
Subscription¶
In OSS, after a customer is subscribed to a service template, the system creates a subscription for the customer.

In the simplest case, a list of resources along with limits in a subscription are copied from the corresponding service template.
Provisioning Resources¶
A subscriber can use a subscription to create (provision) and then use application resources.

Normally, one of the resources in a subscription is auto-provisioned in the previous step, when the subscription is created. During resource provisioning, the APS controller creates a new APS resource and requires the APS connector to provision a respective resource on the application side. When creating a resource, for example a mailbox, the customer can select an offer to assign its parameters to the new resource.
Further Activities¶
How-to Procedures¶
When integrating into the APS ecosystem, you can pursue one or both of the following goals:
- Integrate a management system to monitor, provision, and configure resources on the platform. To do this, follow the Using Platform Services how-to procedures.
- Integrate a cloud application. In this case, the best way to start is to identify the integration points most suitable for you and follow the Integrating Cloud Services how-to procedures.
Concepts¶
If the how-to procedures do not meet all your integration requirements and you need to know more details about the APS ecosystem and platform specifics, dive deeper into the Concepts. You will study there:
- APS Resource Model - the fundamentals of the resource model, APS types, and REST operations.
- Platform Data Models - the fundamentals of service automation on the platform. It explains the OSS and BSS parts of the platform. The former interacts with the integrated application services, and the latter converts the application services to fully automated commercial products.
- Integration Ecosystem - explanation of the APS ecosystem, application deployment schemes, APS resource model, security and performance concepts of the APS protocols.
- Frontend - the concepts of UI integration environment provided by the platform, the store and model based resource management in JavaScript code.
- Application Deployment - explanation of the package structure and application deployment in the platform.
- Product Initialization - preparation of the application services for sale and simplification of that process by means of the product deployment configuration inside an APS package.
- Customization for Sales Channels - building the sales chain of resellers and making some service properties in delegated service plans customizable for the resellers.
- Mail Notifications - explanations of how an application can add and use its own templates for sending email notifications.
- Internationalization and Localization - making an application messages translated to various languages and customizing them to various locales.
- Development Life Cycle - typical project phases, roles, and details of design, development, testing, and troubleshooting.
- Security - explanation of the embedded security model, possible threats, and attack prevention rules.
- Performance - performance analysis and recommendations on the frontend and backend connections.
API and Reference¶
There are a number of reference guides with formal description of APS API and runtime environments that help you reach your goals in the most effective and efficient ways. Use them when you need to identify exactly the syntax of an API call, attributes of a type property, operations of a standard type, or other. Keep the following reference documents handy:
- APS Types - the syntax and content of APS types you can create, as well as the library of the existing APS types you can implement in your code.
- REST Interface - RESTful API calls, protocols, and headers.
- User Interface - the structure of a navigation tree and a view source, as well as the auto-generated documentation on APS JS SDK modules, including widgets, models, stores, and methods.
- PHP Framework - APS PHP framework and library for developing and running the APS connectors (provisioning logic) of APS applications.
Tools and Downloads¶
We recommend that you download, install, and use the APS tools when developing APS applications. The following documents help you arrange your APS development environment, validate and pack your APS project in compliance with the standard:
- Eclipse - a GUI tool recommended to those who are using the Eclipse IDE. It helps creating, validating, deploying, and debugging APS packages in your sandboxes.
- IntelliJ IDEA - a GUI tool recommended to those who are using the IDEA-based IDE. It helps creating, validating, deploying, and debugging APS packages in your sandboxes.
- Command Line Tools - tools used to validate, localize, and build APS packages in the command line interface.
- APS Fiddle - a server-based online tool for validating, testing and debugging JavaScript code.
- Development Portal - helps you go through the whole cycle of developing and testing APS applications by providing a dedicated hosting platform, known as APS Sandbox, to each organization registered in the portal.