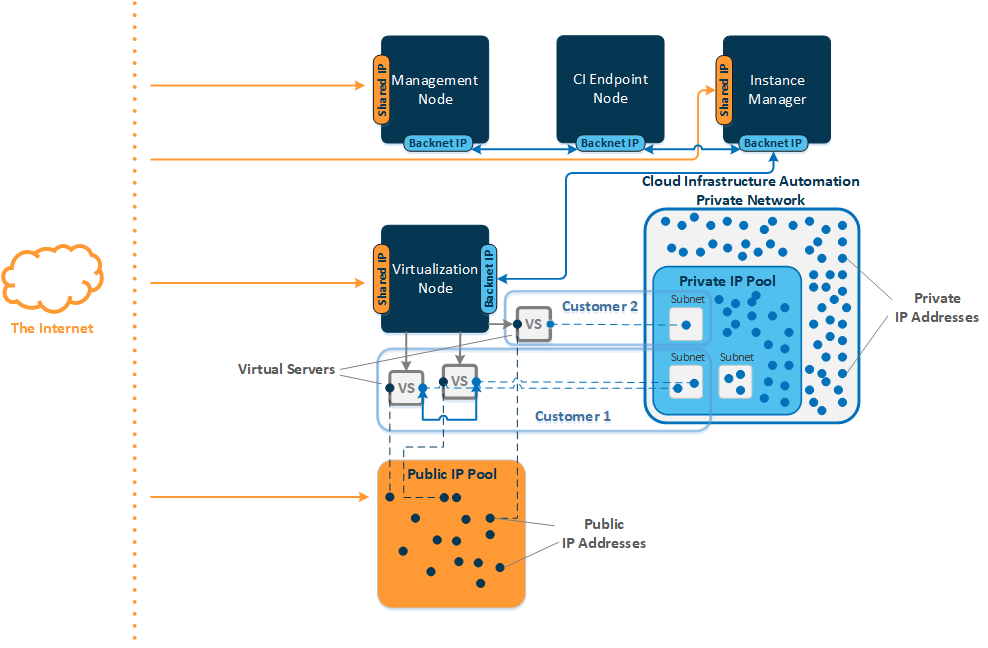
IP Pools
Each network group must contain at least two IP address pools: a public IP pool and a private IP pool.
The public IP pool should contain public IP addresses that your customers will be able to purchase and assign to their virtual servers.
The private IP pool is a range of IP addresses that are automatically assigned to virtual servers once they are created. These IP addresses will be used for internal communications with the Instance Manager and between virtual servers, belonging to a single customer.
When creating IP pools, keep in mind the following:
- Public IP pools may include either IPv4 or IPv6 addresses, while private IP pools may contain IPv4 addresses only.
- All IP pools, that you plan to include in network groups, must belong to different subnetworks. For example, you are not allowed to join one IP pool (with IP addresses from 192.168.101.31 to 192.168.101.154) to the first network group and another IP pool (with IP addresses from 192.168.101.200 to 192.168.101.222) to the second network group if you set the network mask of 255.255.255.0 for both IP pools.