How to Configure VPS Hosting
After deploying the Cloud Infrastructure Automation, you are right away ready for selling Linux container-based VPSs with Plesk. There are two pre-configured VPS Hosting plans and one custom VPS Hosting plan, allowing you to sell VPSs with different hardware configuration. Each VPS Hosting plan has default Linux operating systems to choose from. Your customer can choose whether to buy a VPS with or without Plesk. Each pre-configured hosting plan has a fixed amount of the main hardware resources (CPU, RAM, disk space) and customizable additional resources (backup space, IP addresses), whereas a custom hosting plan has both the main and additional resources customizable.
If you want to sell Windows/Linux virtual machines, you must preliminarily prepare VM OS templates. To learn more about creating VM OS templates, refer to the Preparing OS Templates section.
You do not have to manually configure resource types, there are respective objects in the Cloud Infrastructure Automation that you can configure instead. The resource-object model for VPS Hosting is shown below.
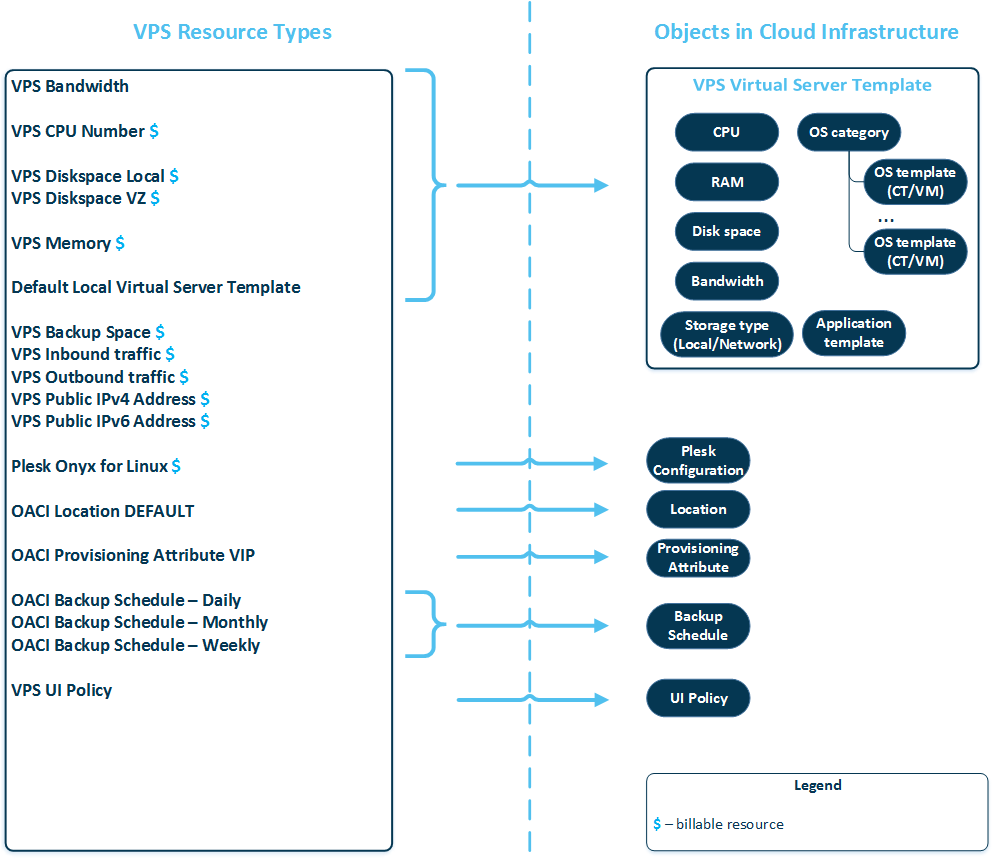
VPS Hosting service template is a set of VPS resources, required for selling virtual private servers. It consists of the following items:
-
Virtual server template defines a virtualization technology, range of operating systems, applications to be installed, a type of storage for a virtual server.
- OS template(s) – an operating system and a standard set of applications to be found right after the installation.
- Application template(s) – a set of software packages re-packaged for use in the Cloud Infrastructure module. You use application templates to add extra software to the existing VPS, for example, MySQL, PostgreSQL and others.
- Plesk configuration(s) – a template which defines Plesk version and a set of Plesk components to install, and specifies administrator's permissions to manage Plesk.
- Backup schedules – schedules according to which automatic VPS backups will be performed.
- UI policy defines which actions customers can perform on their virtual servers (for example, upgrade virtual server, recreate virtual server, manage application templates, configure network and so on). Currently, UI policy is supported only for CCP v1.
- Location defines a geographical location of a virtualization node where a VPS will be provisioned.
- Cloud Infrastructure Automation provisioning attributes are used to distribute virtual servers among the hardware nodes.
You can use default VPS Hosting templates and plans or create your own ones from scratch.
To configure your VPS Hosting resource model from scratch, you need to:
- Prepare your OS templates and application templates and register them in CloudBlue Commerce
- Create your VPS virtual server template, backup schedules, locations, Cloud Infrastructure Automation provisioning attributes, default firewall rules and UI policy.
- If you are planning to sell VPSs with Plesk, you should also prepare Plesk configurations.
- Create your VPS Hosting service template, using Service Template Creation Wizard.
- Create your VPS Hosting service plan, using Service Plan Creation Wizard.
- Configure your VPS Hosting purchase scenario and publish it in the online store.